ELEPHANT MUSEUM
General Information
Project Name: Elephant Museum
Architecture Firm: Bangkok Project Studio
Website: https://www.facebook.com/BangkokProjectStudio
Contact e-mail: bangkokprojectstudio@gmail.com
Firm Location: Bangkok, Thailand.
Completion Year: 2020
Gross Built Area: 5400 sq.m
Project location: Surin Province, Thailand.
Lead Architects: Boonserm Premthada
Lead Architects e-mail: bangkokprojectstudio@gmail.com
Media Provider
Photo credits: Spaceshift Studio
Photographer’s website: http://spaceshiftstudio.com
Photographer’s e-mail: spaceshiftstudio@gmail.com
Video link:
Additional Credits
Engineer : Preecha Suvaparpkul
Clients: Surin Provincial Administration Organisation
Engineering & Construction: Rattanachart Construction Co, Ltd.
Consultants: Surin Provincial Administration Organisation
Elephant Museum
Elephants have a special status in Thailand. They are part of grand royal ceremonies and were war animals for Kings throughout the country’s ancient history.
In addition to being respected, the relationship between elephants and Thai people are unique—being treated as family members rather than pets or labour.
The bond is perhaps strongest in the village of the ethnic Kui in Surin province, north-eastern Thailand.
For many centuries, the community has lived with elephants that their ways of life, from birth to death, can hardly be separated.
Once lush greenery, the forest of Surin was destroyed in favour of cash crops in the last half-century.
The Kui and their elephants suffered extreme droughts, shortages of food and medicinal plants the forest once provided.
Deprived of sustenance, the two displaced to tourist towns begging for food or working in elephant camps, some with unsuitable living conditions.
Elephant Museum is part of Elephant World, a project initiated by the local government to bring the two back to their homeland and to ensure the suitable living conditions for the elephants.
Not only showcasing objects, but the museum shall also portray the voice of the villagers and more than 200 elephants living here—of their long-established familial relationship disapproval of the cruelty of animal exploitation, and of their hope for the future.
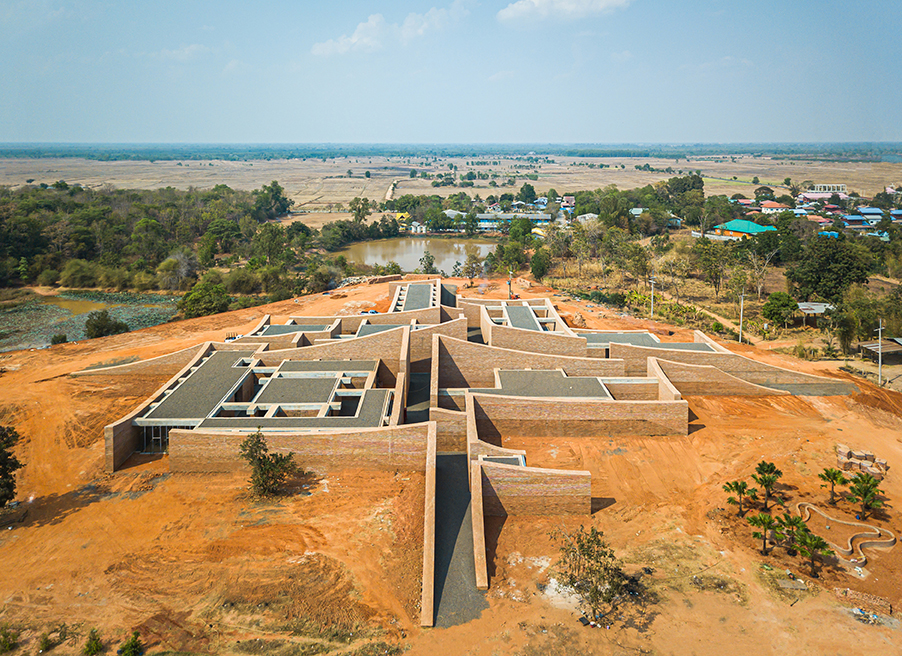
Amidst the vast treeless landscape, curved walls at varying heights sprout from the ground, seemingly opening the building up to visitors of an elephant’s size.
The walls slope and cross one another, revealing gaps that lead visitors to the inside.
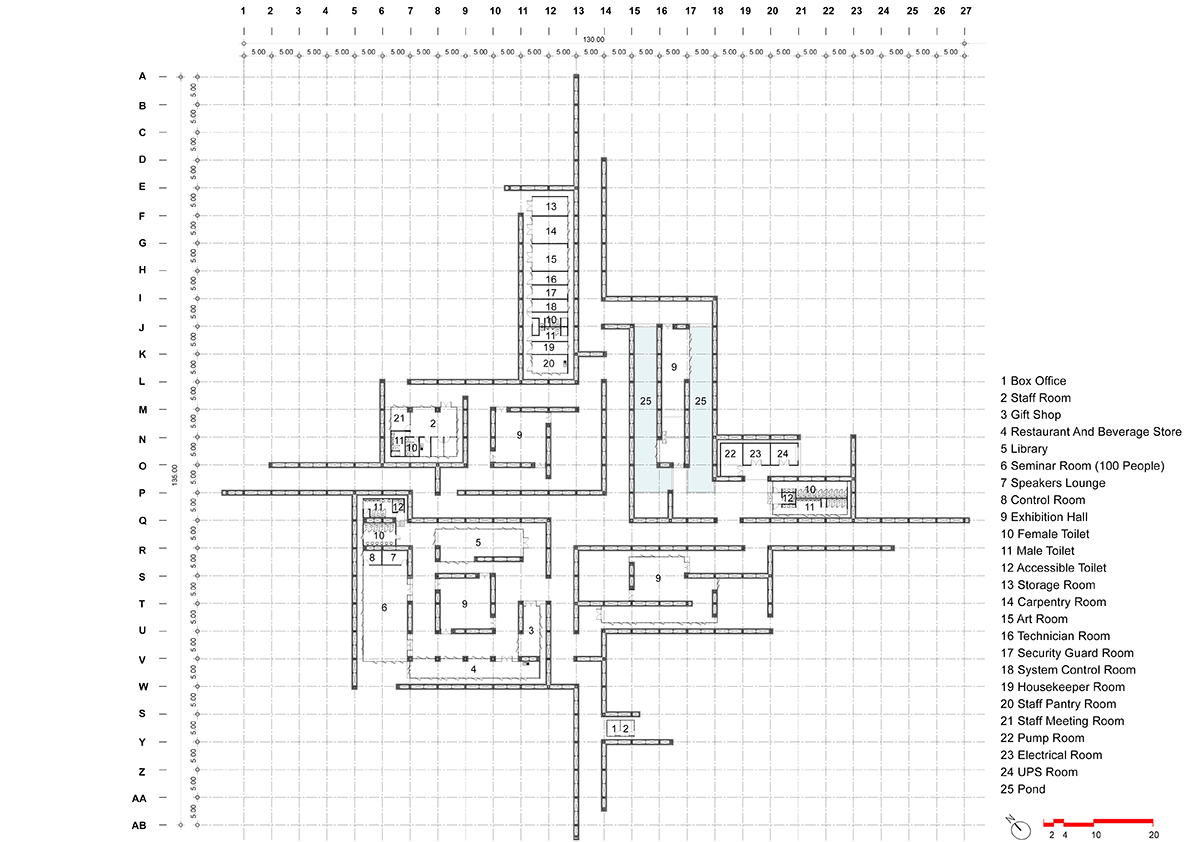
Courtyards of different shapes and sizes open up from the four exhibition galleries.
Some are filled with small pools, some with reddish earth just like the landscape outside.
Different scales of outdoor paths, sheltered space, and open courtyards, recall elements of the area: from elephants, humans, their houses, the ponds they both bathe, to the dirt bath the playful elephants enjoy.
Portraying life under the sun, sunlight is an essential element in the design.
Rooms and paths are brightly lit by sunlight in certain areas and dimmed in others.
The effects change throughout the day, depending on the angle of the sun.
Exhibitions may happen in the courtyards or on exterior walls.
And inside the galleries, one may only find seats to rest and look out at the content displayed outside while reflecting on the coexistence between the two species.
Over 480,0000 fired clay bricks are made by hand from loam found in the area with the technique that has been passed down through generations.
In the town where there are not many job opportunities,
the construction process creates jobs and income for the locals while increasing the value of the often-overlooked local material.
After decades of struggling away from home, the museum shall empower the Kui, the elephants, and the people of Surin.
Its programme and the building process shall encourage them to take pride in their heritage, and restore the dignity of their beloved elephants once again.
At Kui village, Humans live under the same roof as elephants—regarding them as family members rather than pets. This tradition, culture, and wisdom of living together have been passed down for generations.

For centuries, they live in a rural village with the most significant number of domesticated elephants in Thailand.

The low-lying building spans an area of 140x140 metres, with brick walls serving as partitions between outdoor corridors and sheltered rooms such as galleries, a library and other services.

Curved walls at varying heights sprout from the vast landscape. Some slope down to the ground, acting like a door that opens to visitors of an elephant’s size.

Over 480,0000 fired clay bricks are made by hand from loam found in the area. Employing the technique that has been passed down through generations, the construction creates jobs and income for the locals while increasing the value of the often-overlooked local material.

Different scales of outdoor paths, sheltered space, and open courtyards, recall elements of the area: from elephants, humans, their houses, the ponds they both bathe, to the dirt bath the playful elephants enjoy.

Portraying life under the sun, sunlight is an essential design element. Rooms and paths are brightly lit in certain areas and dimmed in others. The effects change throughout the day, depending on the angle of the sun.



The walls slope and cross one another, revealing gaps that lead visitors to the inside.

The brick walls of various heights overlap one another as one walks through to the interior. Each side of a room is surrounded by courtyards of different sizes and shapes.

Reversing outside and inside: Exhibitions may happen on exterior walls. And inside the galleries, one may only find seats to rest and look out at the content displayed outside while reflecting on the coexistence between the two species.

Blurring the boundary between exterior and interior: With varying sizes and shapes of courtyards and rooms, the exhibition could happen either outdoor or indoor.

Not only showcasing artefacts related to the age-old culture of the Kui, but the architecture of the museum also embodies the soul of the Kui and their elephants.
This reflects in elements such as water pools. Water is brought inside the museum, symbolising and reminding locals and visitors of the importance of adequate clean water as the crucial factor for both to survive.

Courtyards of different shapes and sizes open up from the four exhibition galleries. Some are filled with small pools, some with reddish earth just like the landscape outside.

The museum is divided into 4 sections. The main exhibition room is surrounded by outdoor paths, which are in turns encircled by a layer of supporting services: a library, a seminar room and a coffee shop. Meanwhile, another exhibition gallery is flanked by small pools evoking the vital sustenance once deprived from the village.